Choosing a reliable start G-code that primes a dual extruder printer is difficult. There are different extruder prime techniques and my adaptive priming start G-code for Cura uses a mix of these techniques to properly prime the most single/dual nozzle printers.
Prime Techniques
Too little priming leads to inconsistent extrusion and lack of bed adhesion during the first minute of a print before the filament catches up to the nozzle tip.
Too much extrusion leads to blobs sticking to the nozzle and wasted print area.
FDM 3D printing priming techniques have evolved alongside 3D printer hardware to reach higher success rates for extruder priming.
Prime Blob
The Prime Blob is an early technique to quickly unclog and prime the nozzle in a few steps.
-
The nozzle is initially raised far above the bed while heating up.
-
The extruder quickly pushes long length of filament out of the nozzle to create a stream of plastic. The pressure and speed of this rapid extrusion dislodges any stuck plastic on the nozzle to join the plastic stream.
-
The nozzle is simultaneously lowered to the printing layer height and initial printing location.
Ideally the extruded plastic sticks onto the bed and not the nozzle. When nozzle cannot travel off the bed, the prime blob is considered unreliable because the plastic may not contact or stick to the bed early enough which leads to a line of purged plastic loosely sticking to the bed as the nozzle travels to the initial printing location.

The prime blob was most notably used by older Ultimaker printers and explicit generation of prime blob G-code is disabled by default in newer Cura versions.
Some printers such as those made by Prusa and Bambu Labs have gantries that allow the nozzle to move out of the normally printable area. When the prime blob is ejected off to a location off the bed, the chance of failure where the blob is dragged along the bed by the nozzle is lower.
Prime Lines
Prime lines can be as simple as a single straight line, back and forth line sequences, or even a series of curves to try to shake off filament stuck to the nozzle at all angles.
-
The nozzle is raised above the bed while heating up.
-
The nozzle is lowered to the bed at a low height (such as the printing layer height).
-
The nozzle moves along the prime line pattern while extruding plastic.
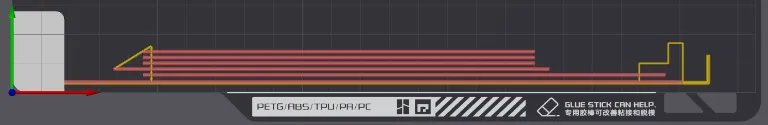
Build plate materials and coatings have become more durable to high temperatures and formulated specifically for superior bed adhesion with the use of steel and PEI coated beds. Newer printers’ prime line routines omit step 1 and keep the nozzle lowered to the bed while heating up. Hot plastic that leaks out of the nozzle due to expansion and gravity sticks to the bed and has a low chance of sticking to the nozzle when the prime line is extruded.
Nozzle Cleaning
Nozzle cleaning is a more recent technique where the nozzle is run over scrubbers of disimilar material than the filament material.
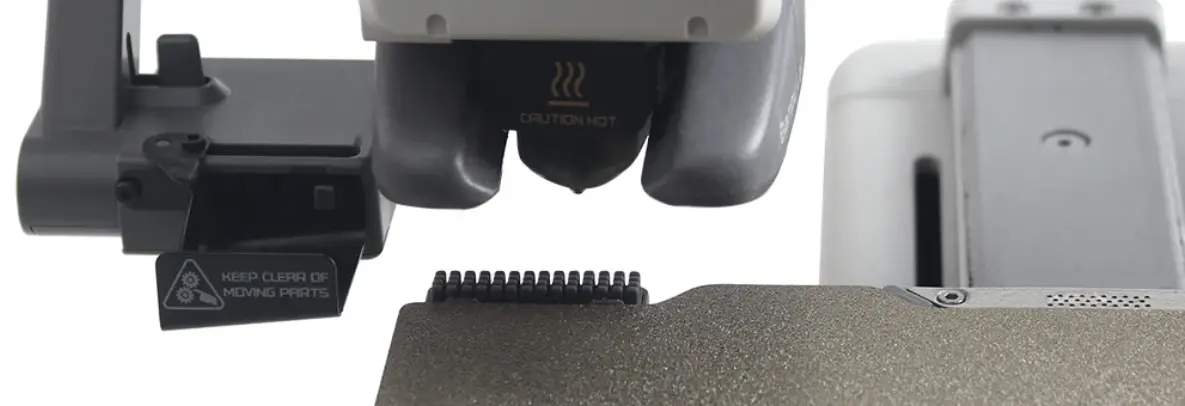

When a scrubber is not available, some printers vary of distance between the nozzle and bed in an attempt to get built up plastic blobs to detach from the nozzle and stick on the bed. Typically the nozzle is heated up and lowered to touch the bed. The nozzle temperature is lowered to a standby temperature where the plastic is not liquid while the nozzle is slowly moved away from the hot bed. This nozzle movement away from the bed is usually in both the vertical and horizontal directions and the part cooling fan can be set to 100% speed to help cool and solidfy the plastic.

Marlin supports the G12 command to invoke a preconfigured nozzle cleaning process.
Adaptive Priming Start G-code for Cura
Interpreted commands in start G-code have been available in PrusaSlicer for years while Cura start G-codes have been forced to be hard coded in the past.
Previously, it was not possible for the start G-code to know which extruders were active, much less what the initial extruder index was. Dual extruder machine configurations in Cura often had repetitive “single” and “dual” machines where the only difference was the start G-code referencing different extruder indexes and priming different number of extruders. Multiple machine profiles in Cura to represent the same machine were hard to maintain, error prone, lagged the slicer, and reset the active print profile when switching between machines.
Cura 5.7.1 and later added support for interpreted variables and math operations in start G-code which opened up the path for smarter start G-code.
Cura start G-code can now use different values in response to slicer variable values through math and ternary operators.
Python syntax ternary operators are supported in start G-code:
a if condition else b
When starting a dual material print, we want the initial extruder to prime last so that the nozzle pressure is immediately used to extrude on the first layer and the nozzle does not leak plastic while waiting to cool and heat. Before math and conditional start G-code, it was not possible to switch to the extruder that was not the initial extruder because we could only use the initial_extruder_nr value which was the opposite of the extruder we wanted. Now we can calculate the unused extruder index with a ternary or modulus operator.
T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} ; switch to NOT initial_extruder_nr nozzle
A potentially serious issue with using a “dual” machine configuration for a single material print in the past was priming and leaving the unused nozzle on. Leaving a nozzle hot led to heat creep and burnt plastic which increases the risk of clogs. This also wasted energy and hampered part cooling. If we know that a nozzle will not be used, it is better to leave that heater off.
If we leave the unused nozzle off, we need to avoid heating and moving the extruder when that tool (nozzle) is selected. We can either use conditional statements to skip the prime movements for the unused nozzle or we can just set all E axis movements to 0 during the unused nozzle’s prime routine. I found it more readable to do the second when the nozzle was unused.
M104 T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} S{material_final_print_temperature if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, 0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} ; Start heating up the NOT initial extruder
G1 X{140-125 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100+125} E{switch_extruder_retraction_amount if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, initial_extruder_nr} F1500
In the above G-code, the tool is heated up and extrudes only if extruders_enabled_count > 1. In a dual extruder machine where we always prime the extruder that is NOT the initial_extruder_nr first, extruders_enabled_count > 1 evaluating to False means that only one extruder will be used in the print and that used extruder’s index is initial_extruder_nr. Therefore we set the temperature and E axis movements to 0 for all commands in the prime routine for the never used extruder that is NOT the initial_extruder_nr.
I use machine_width to prime each extruder as close to the edge of the printable area as possible regardless of machine size.
I use switch_extruder_retraction_amount to prime at least the long retraction distance for each extruder to reset all filament to known locations within the print train.
DXUv2 Start G-code Features
I created the adaptive dual extruder start G-code to prime both nozzles on my dual extruder Ultimaker 2 printer with the DXUv2 upgrade. A preview of the start G-code for both nozzle is depicted below. PrusaSlicer G-code Viewer was used for this preview because it has arc command support while the Ultimaker Cura preview does not. When slicing a model, the Cura preview reflects the G-code produced by the “Cura” side of the slicer which does not include start G-code or post processing changes so the G=code must be exported and dragged back into Cura for an accurate preview.
I included certain characteristics in the start G-code to make the prime routine of dual and single nozzles as reliable as possible.
Reset Filament Location Prime Line

The extruder that is NOT the initial extruder is primed first. The filament may have been retracted by switch_extruder_retraction_amount distance at the end of the last print. The nozzle is heated up and then lowers to the bed diagonally and extrudes filament by switch_extruder_retraction_amount to move the filament to the nozzle tip. Depending on the filament’s starting position within the print train, plastic may or may not actual extruded onto the bed (both of which are fine) which is why the nozzle continuously moves to maintain extruded prime line height.
Avoid Bed Corner Clip
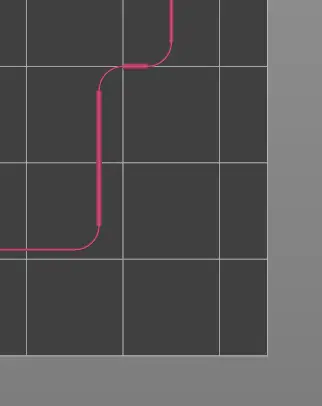
The extruder moves around the exclusion zone of the Ultimaker bed clips in the corners of the printable area while extruding the whole time. Arc movements are used to smooth out the movement and wipe the nozzle from different angles.
Prime Line

The main prime line for the extruder is printed. After the first prime, the filament is almost guaranteed to be at the nozzle tip so we can get a stable prime line.
Break Line and Raise
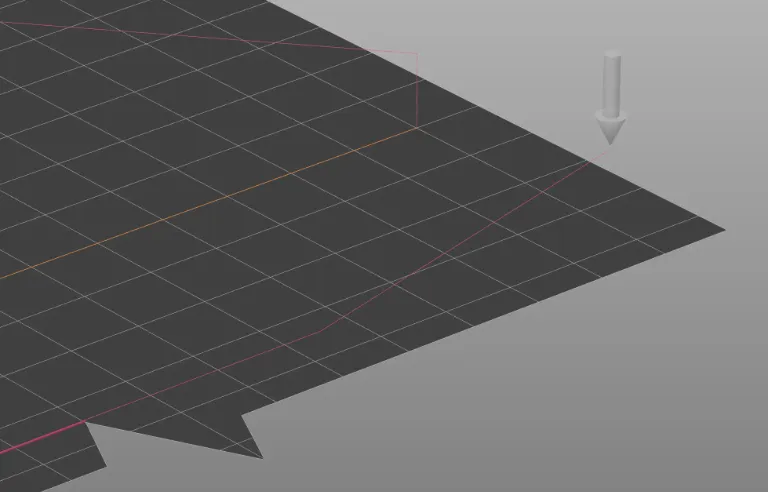
The extruder moves quickly while close to the bed to break the prime line from the nozzle and then raises away from the bed in preparation to switch to the initial extruder. The extruder is cooled down to the standby temperature.
Initial Extruder Prime
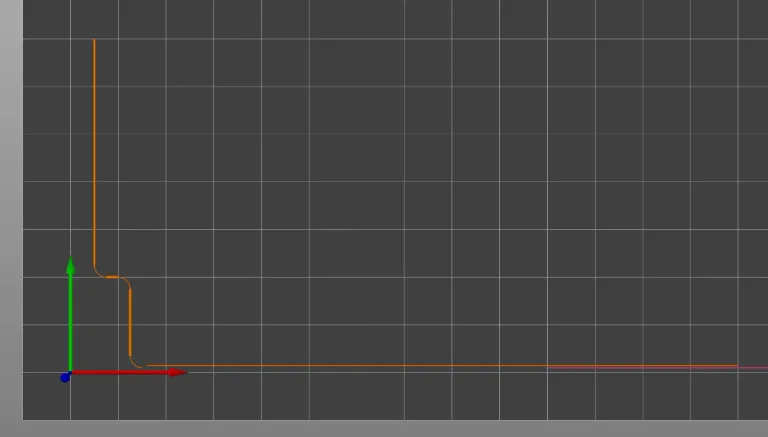
The initial extruder is primed with a similar sequence that is flipped to the other side of the bed. The Reset Filament Location Prime Line is offset to not touch any extrusion by the previous extruder.
Prime Line Wipe and End Prime Location
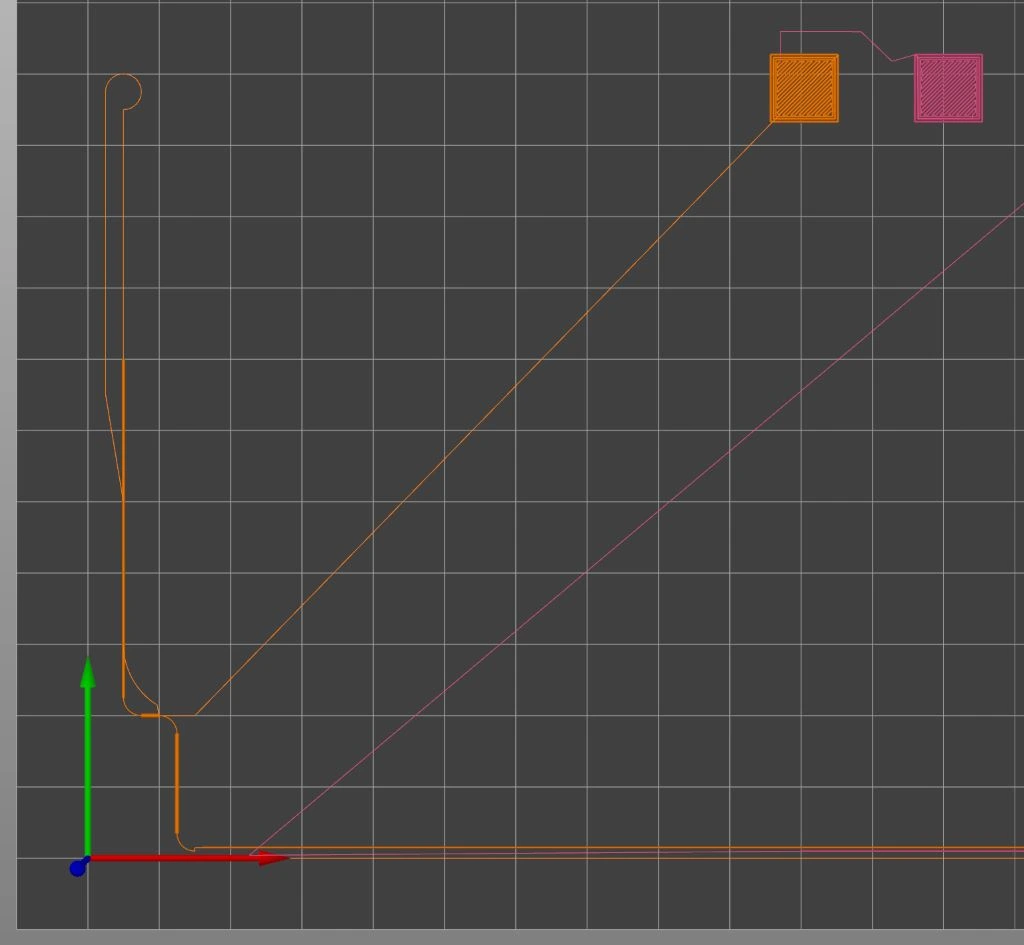
After the break line, a U turn is done with an arc to return the extruder as close to the origin as possible while avoiding the bed clip. The nozzle travels over the previous prime line and is raised slightly to take advantage at the crossing point to wipe the nozzle against previously laid down plastic.
Results
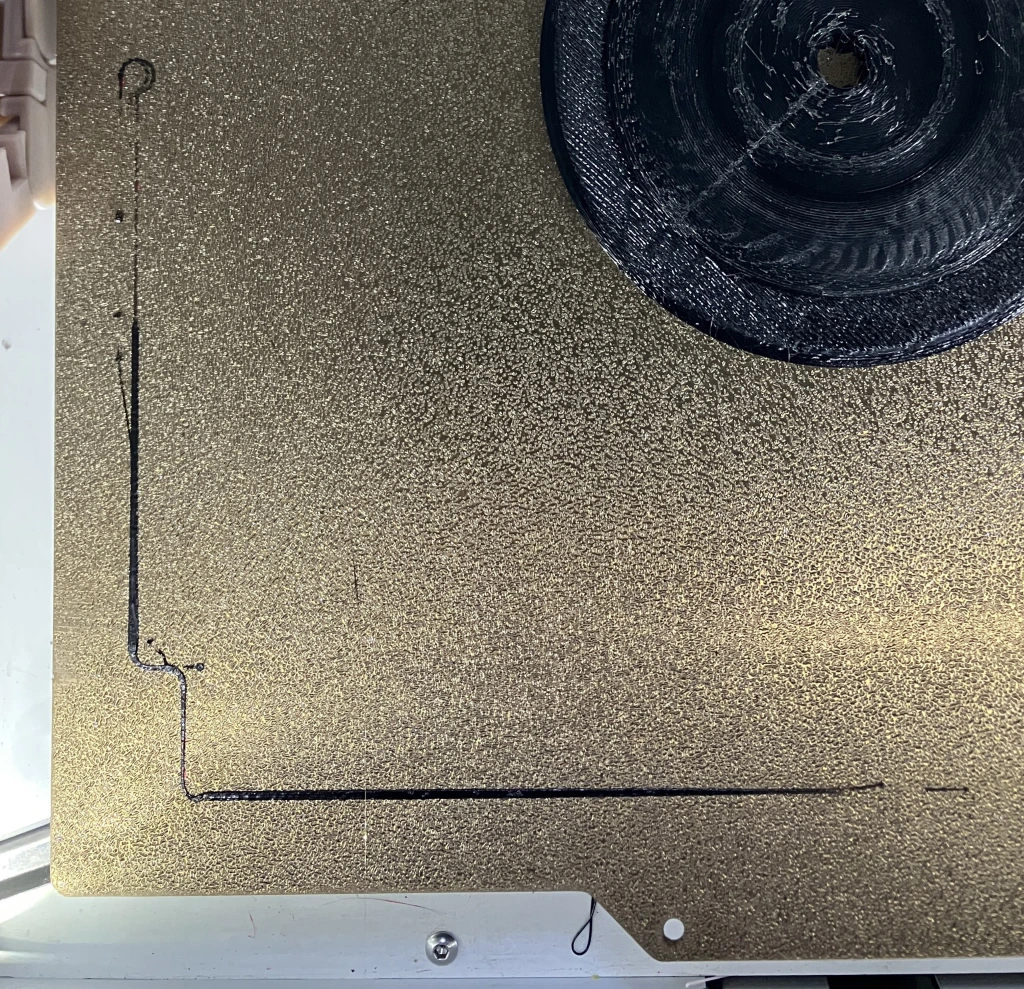

I’ve had great results with this dual nozzle prime routine with very few failures (almost all due to existing user error). It saves time by not heating unused extruders and ensures that the initial extruder is always primed last.
The entire prime line is connected so it is easily removed as a single piece.
Possible Future Improvements
I could heat up the nozzle while it is touching the bed instead of raised in the air. This has the drawback of burning a hole in PEI beds to expose the metal underneath that is within the printable area but could work for glass bed users.
Full Adaptive Dual Extruder Start G-code
My full adaptive dual extruder start G-code is on GitHub as part of the DXUv2 project. The start G-code as of 10/07/24 is:
; Octolapse variables
; Script based on an original created by tjjfvi (https://github.com/tjjfvi)
; An up-to-date version of the tjjfvi's original script can be found
; here: https://csi.t6.fyi/
; Note - This script will only work in Cura V4.2 and above!
; --- Global Settings
; layer_height = {layer_height}
; smooth_spiralized_contours = {smooth_spiralized_contours}
; magic_mesh_surface_mode = {magic_mesh_surface_mode}
; machine_extruder_count = {machine_extruder_count}
; --- Single Extruder Settings
; speed_z_hop = {speed_z_hop}
; retraction_amount = {retraction_amount}
; retraction_hop = {retraction_hop}
; retraction_hop_enabled = {retraction_hop_enabled}
; retraction_enable = {retraction_enable}
; retraction_speed = {retraction_speed}
; retraction_retract_speed = {retraction_retract_speed}
; retraction_prime_speed = {retraction_prime_speed}
; speed_travel = {speed_travel}
; --- Multi-Extruder Settings
; speed_z_hop_0 = {speed_z_hop, 0}
; speed_z_hop_1 = {speed_z_hop, 1}
; retraction_amount_0 = {retraction_amount, 0}
; retraction_amount_1 = {retraction_amount, 1}
; retraction_hop_0 = {retraction_hop, 0}
; retraction_hop_1 = {retraction_hop, 1}
; retraction_hop_enabled_0 = {retraction_hop_enabled, 0}
; retraction_hop_enabled_1 = {retraction_hop_enabled, 1}
; retraction_prime_speed_0 = {retraction_prime_speed, 0}
; retraction_prime_speed_1 = {retraction_prime_speed, 1}
; retraction_retract_speed_0 = {retraction_retract_speed, 0}
; retraction_retract_speed_1 = {retraction_retract_speed, 1}
; retraction_speed_0 = {retraction_speed, 0}
; retraction_speed_1 = {retraction_speed, 1}
; retraction_enable_0 = {retraction_enable, 0}
; retraction_enable_1 = {retraction_enable, 1}
; speed_travel_0 = {speed_travel, 0}
; speed_travel_1 = {speed_travel, 1}
; material_bed_temperature={material_bed_temperature}
; material_print_temperature={material_print_temperature}
; material_print_temperature_layer_0={material_print_temperature_layer_0}
; switch_extruder_retraction_amount_0={switch_extruder_retraction_amount, 0}
; switch_extruder_retraction_amount_1={switch_extruder_retraction_amount, 1}
; DXUv2 improved start priming Gcode for dual nozzles for multi-material print
M355 S1 P25 ; Turn on case light dim
M190 S{material_bed_temperature_layer_0}
T0 ; switch to default extruder
M104 T0 S110
M104 T1 S110
G28 ; Home all
G29 ; Run automatic bed leveling. Comment this line out if auto bed leveling is not desired.
M104 T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} S{material_standby_temperature if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, 0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} ; Preheat not initial extruder to standby temp
M104 T{initial_extruder_nr} S{material_standby_temperature, initial_extruder_nr} ; Preheat initial extruder to standby temp
G21 ; Metric values
G90 ; Absolute positioning
M82 ; Set extruder to absolute mode
M107 ; Start with the fan off
M200 D0 T0 ; Reset filament diameter
M200 D0 T1 ; Reset filament diameter
G0 X200 F7200 ; Move to safe X and Y location from right side after ending ABL homing. Move X before Y to avoid hitting switching lever.
G1 Y150 F7200
; ----
; Prime routine for nozzle that is NOT the initial extruder first
; ----
T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} ; switch to NOT initial_extruder_nr nozzle
M104 T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} S{material_final_print_temperature if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, 0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} ; Start heating up the NOT initial extruder
G0 Z10 F2400 ; move the platform down to 10mm
M109 T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} S{material_print_temperature if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, 0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} ; Heat up and wait for not initial extruder
G0 Y150 F7200 ; Move printhead to safe Y location to move right.
G0 X{machine_width-5 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 5+18} Y1 F7200 ;{machine_nozzle_offset_x,1} cannot be nested so 18 is hardcoded
G0 X{140 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100} Z0.31 F2400 ; lower nozzle
G92 E0 ; reset E location
G1 X{140-125 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100+125} E{switch_extruder_retraction_amount if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, initial_extruder_nr} F1500
G0 Y1 F7200
G92 E0
G{2 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 3} X{140-125-2.5 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100+125+2.5} Y3.5 I0 J2.5 E{0.04 if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0} F7200
G92 E0
G1 E{1.65 if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0} Y17.5
G92 E0
G{3 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 2} X{140-125-5 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100+125+5} Y20 I{-2.5 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 2.5} J0 E{0.04 if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0} F7200
G92 E0
G1 X{140-125-7.5 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100+125+7.5} Y20 E{0.3 if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0}
G92 E0
G{2 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 3} X{140-125-10 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 100+125+10} Y22.5 I0 J2.5 E{0.04 if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0} F7200
G92 E0
G1 Y70 E{3.2 if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0} F1000 ; intro line
M104 T{0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} S{material_standby_temperature if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, 0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1}
G92 E0
G1 E-{switch_extruder_retraction_amount if extruders_enabled_count > 1 else 0, 0 if initial_extruder_nr>0 else 1} F1200 ; retract
G0 Y105 F18000 ; break line
G0 Y150 Z10 F2400 ; raise nozzle
; ----
; Prime routine for initial nozzle
; ----
T{initial_extruder_nr} ; switch to initial_extruder_nr nozzle
M104 T{initial_extruder_nr} S{material_final_print_temperature, initial_extruder_nr} ; Start heating up the initial extruder
G0 Z10 F2400 ; move the platform down to 10mm
M109 T{initial_extruder_nr} S{material_print_temperature, initial_extruder_nr} ; Heat up and wait for not initial extruder
G0 Y150 F7200 ; Move printhead to safe Y location to move right.
G0 X{machine_width-5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 5+18} Y1.5 F7200 ; {machine_nozzle_offset_x,1} cannot be nested so 18 is hardcoded
G0 X{140 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100} Z0.31 F2400 ; lower nozzle
G92 E0 ; reset E location
G1 X{140-124 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+124} E{switch_extruder_retraction_amount, initial_extruder_nr} F1500
G1 X{140-125 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125} F7200
G0 Y1 F7200
G92 E0
G{2 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 3} X{140-125-2.5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+2.5} Y3.5 I0 J2.5 E0.04 F7200
G92 E0
G1 E1.65 Y17.5
G92 E0
G{3 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 2} X{140-125-5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+5} Y20 I{-2.5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 2.5} J0 E0.04 F7200
G92 E0
G1 X{140-125-7.5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+7.5} Y20 E.3
G92 E0
G{2 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 3} X{140-125-10 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+10} Y22.5 I0 J2.5 E0.04 F7200
G92 E0
G1 Y70 E3.2 F1000 ; intro line
G92 E0
G0 Y105 F18000 ; break line
; ----
; Final prime and wipe sequence for initial extruder
; ----
G{3 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 2} X{140-125-10-2.5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+10+2.5} Y107.5 Z0.48 I0 J2.5 F18000
M400 ;finish all moves
M104 T{initial_extruder_nr} S{material_print_temperature, initial_extruder_nr} ; Wait for initial nozzle to reach temp if needed.
G0 Y75 F18000
G0 Y65 F7200
G0 X{140-125-10 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+10} Y50 F7200
G92 E0
G1 Y40 Z0.4 E0.25 F7200
G92 E0
G1 Y30 E0.5 F7200
G{3 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 2} X{140-125-5 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else 100+125+5} Y20 Z0.4 I{10 if initial_extruder_nr<1 else -10} J0 F18000
G0 X15 Y20 Z0.36 F18000 ;move to start position
G0 F18000 ;set starting acceleration
M104 T{initial_extruder_nr} S{material_print_temperature_layer_0, initial_extruder_nr} ; Start heating to first layer temp
M355 S1 P150; Turn on case light brighter
;end of DXUv2 prime routine

